Last updated: 19th June 2024
Using Excel, you can now maintain complex data structures, create graphs and more. But, do you know you can use Excel data in a Windows Forms Application. Here in this article, I am going to show you how to read an Excel file or import data from Excel in your Windows Forms application using C# and VB.NET. In-addition, I'll show you how to save the imported data into a table in SQL Server.➡️ I am sharing three examples here showing how to read and extract data from Excel and how and where you can use this data.
1) The first example imports data from Excel and populates a Combo box.
2) The second example imports data from Excel and binds the data to a DataGridView control.
3) The third example shows how to insert the extracted data (from Excel) into an SQL Server database table.
➡️ To read an Excel file (either .xlsx or .xls) from a Windows application, you will have to include Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel namespace in your project. The namespace provides methods and properties that will allow us to interact with an Excel file and manipulate its data.
So, lets get on with it.
First, create a new Windows Form Application project, choosing your preferred language. I have written code in both C# and VB.NET.
Add "Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel" Reference
After you have created the project, add a reference.
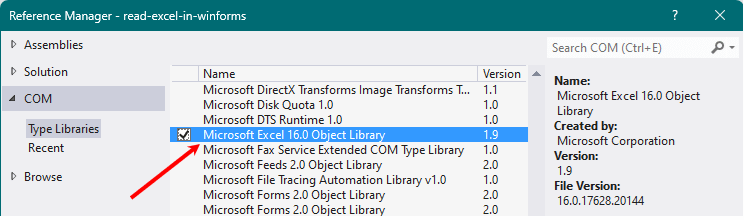
From the top menu (in your projects IDE), select the "Project" tab and choose Add Reference… It will open the "Add Reference" window. Select the COM tab and find "Microsoft Excel 12.0 Object Library" library (or a higher version) from the list. Click Ok.
See the below image. I have Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library.
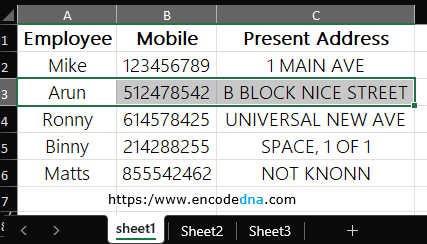
Here's a sample data in an Excel file. Assuming, the data is in "Sheet1".
Import the Namespace in your Project
The namespace Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel has all the necessary methods and properties that you'll need to connect with your Excel file. But first, you will have to import or use the namespace in your project.
For C#
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
For Vb
Imports Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel
Note: To access data from a Word file, first add Microsoft Word 12.0 Object Library reference and import or use the namespace. For example,
using Word = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word;
I have also added OpenFileDialog tool in the form, to select an Excel file from my computer. Therefore, go to design mode in your form. In the toolbox find OpenFileDialog control (its under "All Windows Form") and drag and drop it on the form.
1) Read Excel and Populate Data in a Combo Box
The first example shows you how to select and read an Excel file and populate Combo Box with the data.
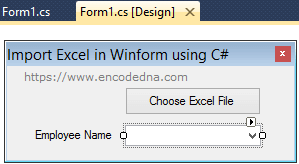
In your form, add a button and a Combo Box and name it cmbEmp. See the image.
Double click the button and open the code behind window. We’ll write our code inside the buttons click event.
Clicking the button will open a file dialog box. Selecting the file will call a private procedure, which will read the data from the first column (Employee) in Sheet 1. Finaly, populate the "combo box" with the data.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Windows.Forms; using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; namespace read_excel { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } // CREATE EXCEL OBJECTS. Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkBook; Excel.Worksheet xlWorkSheet; string sFileName; int iRow, iCol = 2; // OPEN FILE DIALOG AND SELECT AN EXCEL FILE. private void cmdSelect_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { OpenFileDialog1.Title = "Excel File to Edit"; OpenFileDialog1.FileName = ""; OpenFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel File|*.xlsx;*.xls"; if (OpenFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { sFileName = OpenFileDialog1.FileName; if (sFileName.Trim() != "") { readExcel(sFileName); } } } // GET DATA FROM EXCEL AND POPULATE COMB0 BOX. private void readExcel(string sFile) { xlApp = new Excel.Application(); xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile); // WORKBOOK TO OPEN THE EXCEL FILE. xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]; // NAME OF THE SHEET. for (iRow = 2; iRow <= xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count; iRow++) // START FROM THE SECOND ROW. { if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value == null) { break; // BREAK LOOP. } else { // POPULATE COMBO BOX. cmbEmp.Items.Add(xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value); } } xlWorkBook.Close(); xlApp.Quit(); } } }📋
Note: Alway use try… catch in your code to handle exceptions.
➡️ You can work with multiple worksheets data. Simply add the name of the "Sheet" in your code.
Option Explicit On Imports Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel ' EXCEL APPLICATION. Public Class frmImportExcel ' CREATE EXCEL OBJECTS. Dim xlApp As Excel.Application Dim xlWorkBook As Excel.Workbook Dim xlWorkSheet As Excel.Worksheet Private Sub cmdSelect_Click(sender As System.Object, e As System.EventArgs) Handles cmdSelect.Click With OpenFileDialog1 .Title = "Excel File to Edit" ' DIALOG BOX TITLE. .FileName = "" .Filter = "Excel File|*.xlsx;*.xls" ' filte only excel files using file type. Dim sFileName As String = "" If .ShowDialog() = DialogResult.OK Then sFileName = .FileName If Trim(sFileName) <> "" Then readExcel(sFileName) ' READ EXCEL DATA. End If End If End With End Sub ' GET DATA FROM EXCEL AND POPULATE COMB0 BOX. Private Sub readExcel(ByVal sFile As String) xlApp = New Excel.Application xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile) ' WORKBOOK TO OPEN THE EXCEL FILE. xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets("Sheet1") ' NAME OF THE WORK SHEET. Dim iRow As Integer For iRow = 2 To xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count If Trim(xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value) = "" Then Exit For ' BAIL OUT IF REACHED THE LAST ROW. Else ' POPULATE COMBO BOX. cmbEmp.Items.Add(xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value) End If Next xlWorkBook.Close() : xlApp.Quit() ' CLEAN UP. (CLOSE INSTANCES OF EXCEL OBJECTS.) System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp) : xlApp = Nothing System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkBook) : xlWorkBook = Nothing System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkSheet) : xlWorkSheet = Nothing End Sub End Class📋
2) Populate a DataGridView Control with the Excel Data
You can populate a DataGridView control dynamically with the Excel data. It is very simple. The data extraction part is similar to the one I have explained in the above example.
First, add a DataGridView control to the form. You can find this control in the toolbox.
Now let’s see the code. The form already has the OpenFileDialog control to select files.
I am extending my previous example. You’ll just have to modify the readExcel() method. The method takes a parameter in the form of the file name.
private void readExcel(string sFile)
{
xlApp = new Excel.Application();
xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile);
xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets["Sheet1"];
// FIRST, CREATE THE DataGridView COLUMN HEADERS.
int iCol;
for (iCol = 1; iCol <= xlWorkSheet.Columns.Count; iCol++)
{
if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[1, iCol].value == null)
{
break; // BREAK LOOP.
}
else
{
DataGridViewColumn col = new DataGridViewTextBoxColumn();
col.HeaderText = xlWorkSheet.Cells[1, iCol].value;
int colIndex = dataGridView1.Columns.Add(col); // ADD A NEW COLUMN.
}
}
// ADD ROWS TO THE GRID.
for (iRow = 2; iRow <= xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count; iRow++) // START FROM THE SECOND ROW.
{
if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value == null)
{
break; // BREAK LOOP.
}
else
{
// CREATE A STRING ARRAY USING THE VALUES IN EACH ROW OF THE SHEET.
string[] row = new string[] { xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value,
xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 2].value.ToString(),
xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 3].value };
// ADD A NEW ROW TO THE GRID USING THE ARRAY DATA.
dataGridView1.Rows.Add(row);
}
}
xlWorkBook.Close();
xlApp.Quit();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkBook);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkSheet);
}📋I am creating the DataGridView header by running a for loop using the columns in the Excel file. Next, I am running another loop to extract rows in the Excel Sheet and assigning the values to the Grid.
Private Sub readExcel(ByVal sFile As String)
xlApp = New Excel.Application
xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile)
xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
' FIRST, CREATE THE DataGridView COLUMN HEADERS.
Dim iCol As Integer
For iCol = 1 To xlWorkSheet.Columns.Count
If Trim(xlWorkSheet.Cells(1, iCol).value) = "" Then
Exit For ' BAIL OUT IF REACHED THE LAST COL.
Else
Dim col = New DataGridViewTextBoxColumn()
col.HeaderText = xlWorkSheet.Cells(1, iCol).value
Dim colIndex As Integer = dataGridView1.Columns.Add(col) ' ADD A NEW COLUMN.
End If
Next
' ADD ROWS TO THE GRID.
Dim iRow As Integer
For iRow = 2 To xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count
If Trim(xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value) = "" Then
Exit For ' BAIL OUT IF REACHED THE LAST ROW.
Else
' CREATE A STRING ARRAY USING THE VALUES IN EACH ROW OF THE SHEET.
Dim row As String() = New String() { _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value, _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 2).value.ToString(), _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 3).value}
' ADD A NEW ROW TO THE GRID USING THE ARRAY DATA.
dataGridView1.Rows.Add(row)
End If
Next
xlWorkBook.Close() : xlApp.Quit()
' CLEAN UP. (CLOSE INSTANCES OF EXCEL OBJECTS.)
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp) : xlApp = Nothing
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkBook) : xlWorkBook = Nothing
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkSheet) : xlWorkSheet = Nothing
End Sub📋3) Save Excel Data to SQL Server Database Table
You might also want to save the Excel data (as it is) to an SQL Server database table.
Create a table first with three columns and name it Employee.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Employee]( [EmpName] [varchar](50) NULL, [Mobile] [bigint] NULL, [Address] [varchar](200) NULL ) ON [PRIMARY]📋
Now the code.
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; using System.Data.SqlClient; // FOR DATA CONNECTION. private void saveExcelData(string sFile) { xlApp = new Excel.Application(); xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile); xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]; string sInsert = ""; // GET VALUES FROM EXCEL AND CREATE SQL INSERT QUERY. for (iRow = 2; iRow <= xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count; iRow++) // START FROM THE SECOND ROW. { if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value == null) { break; // BREAK LOOP. } else { if (sInsert.Trim() == "") { sInsert = "INSERT INTO dbo.Employee1 (EmpName, Mobile, Address) " + "VALUES ('" + xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value + "', " + xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 2].value + ", '" + xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 3].value + "')"; } else { sInsert = sInsert + System.Environment.NewLine + "INSERT INTO dbo.Employee1 (EmpName, Mobile, Address) " + "VALUES ('" + xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value + "', " + xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 2].value + ", '" + xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 3].value + "')"; } } } xlWorkBook.Close(); xlApp.Quit(); System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp); System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkBook); System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkSheet); // CREATE DATABASE PROPERTIES. using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection("Data Source=DNA;Persist Security Info=False;" + "Initial Catalog=DNA_Classified;User Id=sa;Password=demo;Connect Timeout=30;")) { if (sInsert.Trim() != "") { SqlCommand command = con.CreateCommand(); try { con.Open(); // OPEN THE CONNECTION. command.CommandText = sInsert; // INSERT THE DATA. command.ExecuteNonQuery(); MessageBox.Show("Data Saved"); } finally { con.Close(); } } } }📋
Inside the for loop extract Excel data row by row and create the INSERT query with values. Create a database connection and insert the data to the database table.
Private Sub saveExcelData(ByVal sFile As String)
xlApp = New Excel.Application
xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile)
xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim iRow As Integer
Dim sInsert As String = ""
' GET VALUES FROM EXCEL AND CREATE SQL INSERT QUERY.
For iRow = 2 To xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count
If Trim(xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value) = "" Then
Exit For
Else
If Trim(sInsert) = "" Then
sInsert = "INSERT INTO dbo.Employee1 (EmpName, Mobile, Address) " & _
"VALUES ('" + xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value + "', " & _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 2).value.ToString + ", '" & _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 3).value.ToString + "')"
Else
sInsert = sInsert & vbCrLf & _
"INSERT INTO dbo.Employee1 (EmpName, Mobile, Address) " & _
"VALUES ('" + xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 1).value + "', " & _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 2).value.ToString + ", '" & _
xlWorkSheet.Cells(iRow, 3).value + "')"
End If
End If
Next
xlWorkBook.Close() : xlApp.Quit()
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp) : xlApp = Nothing
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkBook) : xlWorkBook = Nothing
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkSheet) : xlWorkSheet = Nothing
// CREATE DATABASE PROPERTIES.
Using con As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection("Data Source=DNA;Persist Security Info=False;" & _
"Initial Catalog=DNA_Classified;User Id=sa;Password=demo;Connect Timeout=30;")
If Trim(sInsert) <> "" Then
Try
Dim command As SqlCommand = con.CreateCommand()
con.Open()
command.CommandText = sInsert
command.ExecuteNonQuery()
MessageBox.Show("Data Saved")
Finally
con.Close()
End Try
End If
End Using
End Sub📋