Last Updated: 28th October 2025
Yes, an SQL query can include both WHERE and HAVING clauses, and they often work together to filter data at different stages of query execution.The WHERE clause filters individual rows before any grouping or aggregation takes place.
The HAVING clause filters grouped results after aggregate functions like SUM(), COUNT(), or AVG() have been applied.
👉 Learn more about "Commonly Used Aggregate Functions with Examples"
Now, let us assume, I have a table named dbo.books and it has 5 columns and few rows of data. See the below image.
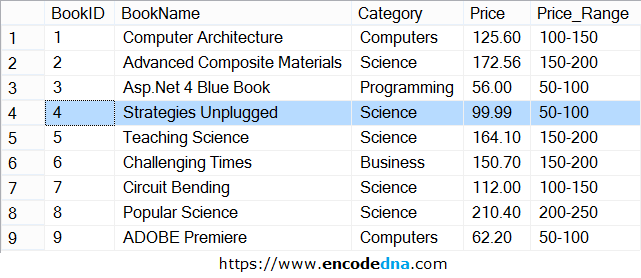
👉 First, let's break it down with two separate examples to see how the WHERE and HAVING clauses work in SQL.
1) Using WHERE
SELECT Category, SUM(Price) AS [Total_Price] FROM dbo.Books WHERE Price > 150 GROUP BY Category
In the query above, the goal is to calculate the total price for each book category, but only for those records where the individual book price is greater than 150.
Since we're using the SUM() function to aggregate prices by category, we must include a GROUP BY clause to group the results accordingly. Without GROUP BY, SQL Server wouldn't know how to organize the data for aggregation, and the query would result in an error.
2) Using HAVING
SELECT Category, SUM(Price) AS [Total Price] FROM dbo.Books GROUP BY Category HAVING SUM(Price) > 150
In the second query, I am using the HAVING clause. Its on an aggregate function (SUM()). Unlike the WHERE clause, this query first returns the rows by grouping it and then filters it with the total sum using the HAVING clause.
🚀 Mastering SQL Server HAVING Clause: Syntax, Usage & Examples
Now, I want to do something similar (using both the above queries) in a single query. See this query first.
SELECT Category, SUM(Price) AS [Total Price] FROM dbo.Books WHERE Category IN ('Computers', 'Science', 'Programming') GROUP BY Category
Output (image)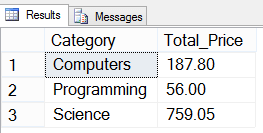
It returns the sum of price for individual categories. I am filtering the categories using the WHERE clause. I don’t want all the categories.
Now suppose, I want to filter it further to get the rows where sum of the price is greater (>) than 150. Not all the rows.
Unfortunately, I cannot do this in an SQL query! 👇
SELECT Category, SUM(Price) Total_Price FROM dbo.Books WHERE Category IN ('Computers', 'Science', 'Programming') AND SUM(Price) > 150 -- This is incorrect. It will throw an error. GROUP BY Category
Therefore, I'll have to use the HAVING clause along with the WHERE clause in the above query.
🚀 SQL Server HAVING Clause Explained with Practical Examples
Using WHERE and HAVING in a single SQL query
SELECT Category, SUM(Price) Total_Price FROM dbo.Books WHERE Category IN ('Computers', 'Science', 'Programming') GROUP BY Category HAVING SUM(Price) > 150
Output
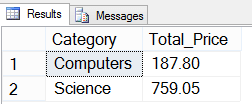
-------------------
🚀 Here's a list of Top 5 popular SQL Server posts.
1) How to find and remove Duplicate rows in a Table using SQL Server ROW_NUMBER() and CTE: Duplicate rows in tables can be very annoying for DBA’s and programmers, as it raises many uncomfortable questions about the authenticity of data in a database. The matter gets worse when company auditors complain about irregularities in the balance sheet etc.
2) How to convert Rows into Columns using SQL Server PIVOT OR how to use PIVOT in SQL Server: Ever wondered how you can convert data from rows to columns in SQL Server. We are talking about an SQL query, which will transform records from multiple rows into columns. Using SQL Server PIVOT, we can efficiently rotate a table’s data to show a summarized result.
3) Insert Multiple rows with a Single INSERT Statement using SQL Server Table Value Constructor: While managing an Inventory management System for an organization, I have came across a situation where I had to perform bulk upload on a table in SQL Server. Bulk upload requires inserting multiple rows of data in a table.
4) How to Convert Month Number in a Date to Month Name in SQL Server: Let us assume I have a Sales table with sales data for each month. Every day sales is stored in the table with columns such as date, quantity, price etc. I want to get the total sales for every month. Now since I have a column with “date” data type, I want to convert the month number in the date to Month Name (like February, March etc.). Find out how this is done in SQL Server.
5) SQL Server CHARINDEX Function with Examples: The primary use of an SQL Server CHARINDEX function is to find the first or starting location of an expression or characters in a given string. To make it simple, it is like searching a specified character or characters in a string.
