Using "null" with the "equality" operator
You can use the equality (==) operator in JavaScript to check if a variable is undefined or null. For example,
let myName;
if (myName == null)
{
alert ('The variable is null!');
}I have declared a variable called myName. However, I have not assigned any value to it. I am using the "null" keyword with the equality (==) operator to check if the variable is null.
Using the "undefined" type
In some cases, you can use the undefined keyword to check the variables status. For example,
let myName;
if (myName == undefined)
{
alert ('Its undefined');
}It is safe to use the undefined type in your JavaScript code to check the status of a variable. All new browsers support this type.
💡 Remember, a with a blank value is not undefined or null.
var myName = '';
The variable myName has a value (blank, I would say), but it is neither null nor undefined.
Uncaught ReferenceError: variable is not defined
Your browser console may also sometimes show an error and would say, Uncaught ReferenceError: some_variable is not defined. See the bottom of the image.
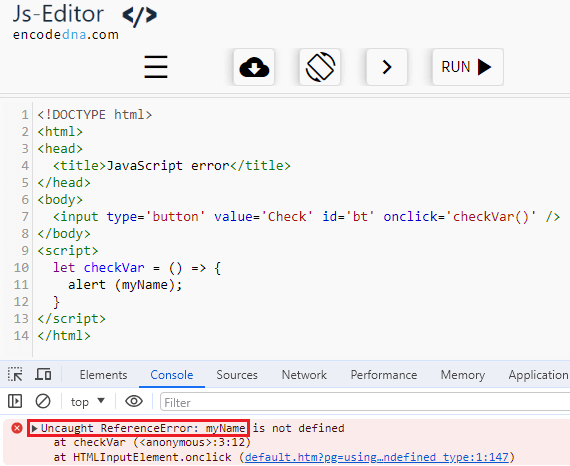
Don’t confuse this error with the undefined error that I have explained above. Both are different and have different meanings. In this case, I have not declared (or defined) the variable myName anywhere in my JS code. It does not know if it’s a string, number or a Boolean.
So, to check if a variable is undefined or null, you must first declared or define the variable in your code.
