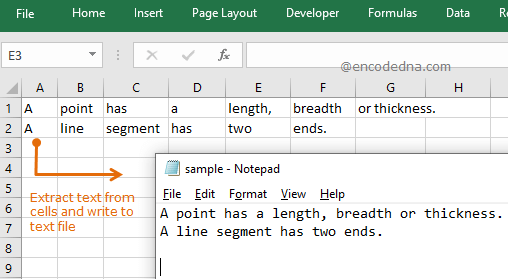
The two images below explain what the macro will actually do. In the first image, I have a table in Excel and the macro writes the entire table’s data in a .txt file. The second image shows how the macro extracts data from each cell and row and writes it (as it is line-by-line) in a .txt file.
Image 1 👇
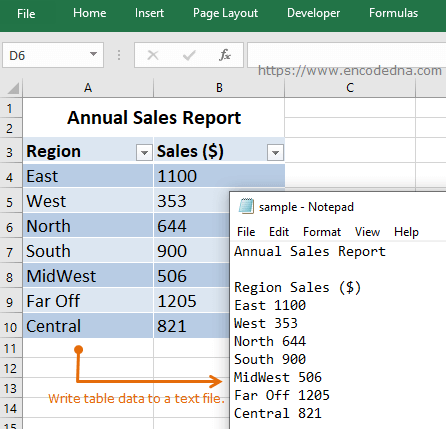
Image 2 👇
Here’s the macro.
Option Explicit Dim objFso As New FileSystemObject ' Create FSO object. Dim objTS As TextStream ' For TextStream object. Dim sFolder As String Private Sub Worksheet_Activate() write_to_file End Sub Sub write_to_file() ' Get used range rows count in your worksheet. Dim iTotalRows As Integer iTotalRows = Worksheets("sheet1").UsedRange.Rows.Count ' Get used range columns count in your worksheet. Dim iTotalCols As Integer iTotalCols = Worksheets("sheet1").UsedRange.Columns.Count Dim iRowCnt, iColCnt As Integer Dim sText As String ' Iterate (or loop) through each row and column. For iRowCnt = 1 To iTotalRows For iColCnt = 1 To iTotalCols ' Store the data in a variable. sText = sText & Worksheets("Sheet1").Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt) & " " Next iColCnt sText = sText & vbCrLf ' For next row. Next iRowCnt ' Return a TextStream object using the FSO CreateTextFile() method. sFolder = "d:\fixtures" Set objTS = objFso.CreateTextFile(sFolder & "\sample.txt") objTS.WriteLine sText ' Finally, write the text in the file. objTS.Close ' Close the file. End Sub
What am I doing here?
I created two objects in the beginning of the macro. The first is the FileSystemObject (or FSO) and second object is of the TextStream class. Both classes provided two crucial methods, which I have used at the end of the procedure.
' method 1: CreateTextFile() of FileSystemOject.
Set objTS = objFso.CreateTextFile(sFolder & "/sample.txt")
' method 2: WriteLine of TextStream class.
objTS.WriteLine sText
Next, I’ll get the worksheets used range, or the rows and columns which have some data. (the blanks rows are ignored)
iTotalRows = Worksheets("sheet1").UsedRange.Rows.Count
iTotalCols = Worksheets("sheet1").UsedRange.Columns.Count
The used range can have a table or simply some data in each cell.
Later, I’ll loop through (using For ... next loop) each row and its cells to extract data and store it in a variable named sText. Look carefully, I have added a blank text (or string) like this & " ", while reading data in cells. This is to add a space after each text. In-addition, to write data in the next row, I have added vbCrlf.
Finally, I am writing the data in a file named sample.txt in a folder.
sFolder = "d:\fixtures"
Set objTS = objFso.CreateTextFile(sFolder & "\sample.txt")
objTS.WriteLine sText
Note: If a text file with the same name already exists in the folder, the macro will overwrite the contents with the data it extracted from the worksheet.
Do not forget to close the file, once everything is done.
objTS.Close
I have not defined any range in my Excel worksheet. All I have done is provide the name of the active worksheet, like sheet1, and the macro will do the remaining. It will read data, as it is, from each row and cell, and write the data in a file.
