image
1) Pull Data from a Specific Sheet in another Workbook
Let us assume, I have an Excel file (the source file), which has data in tabular format.
To extract data from another workbook using a Macro, you have to provide the workbook name and full path to a procedure (or a piece of code) to process. You can hard code the file name and path, store it in a variable, and then process it. However this example, I am using the FileDialog() method to select the source file (the Workbook).
Since I am using the FileDialog method, I need an ActiveX button control on my worksheet. So, first you need to add a button in your worksheet. Write the code in the button’s click event.
Option Explicit
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
' Create and set the file dialog object.
Dim fd As Office.FileDialog
Set fd = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker)
With fd
.Filters.Clear
.Title = "Select an Excel File"
.Filters.Add "Excel Files", "*.xlsx?", 1
.AllowMultiSelect = false
Dim sFilePath As String
If .Show = True Then
sFilePath = .SelectedItems(1)
End If
End With
If sFilePath <> "" Then
readExcelData (sFilePath)
End If
End Sub
Sub readExcelData(sTheSourceFile)
On Error GoTo ErrHandler
Application.ScreenUpdating = False ' Do not update the screen.
Dim src As Workbook
Set src = Workbooks.Open(sTheSourceFile, True, True) ' Open the source file.
Dim iRowsCount As Integer ' Get the total Used Range rows in the source file.
iRowsCount = src.Worksheets("sheet1").UsedRange.Rows.Count
Dim iColumnsCount As Integer ' Get the total Columns in the source file.
iColumnsCount = src.Worksheets("sheet1").UsedRange.Columns.Count
Dim iRows, iCols, iStartRow As Integer
iStartRow = 0
' Now, read the source and copy data to the master file.
For iRows = 1 To iRowsCount
For iCols = 1 To iColumnsCount
Cells(iRows + iStartRow, iCols) = src.Worksheets("Sheet1").Cells(iRows, iCols)
Next iCols
Next iRows
iStartRow = iRows + 1
iRows = 0
' Close the source file.
src.Close False ' False, so you don't save the source file.
Set src = Nothing
ErrHandler:
Application.EnableEvents = True
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubFirst, I am creating a FileDialog object to open a file dialog box. I can select a workbook from anywhere in the computer. Next, I am calling the “readExcelData()” procedure, where I have the code to read the source file.
What’s inside the readExcelData()? The procedure takes a parameter (or an argument), the source file name and its full path. Now, look at this property Application.ScreenUpdating, which I have set as “false”. Setting this property value as false ensures that the macro runs fast and smooth, since it will not update the screen. Read more about this property here. You must set the value as true after executing the code.
Next, I am opening the source file. It’s in readonly state, which means, during this whole process, you cannot do anything in the source file even if its open.
Set src = Workbooks.Open(sTheSourceFile, True, True) ' Open the source file.
Once I have access to the Excel file, I’ll get the total row and column count and read all the table data in the file.
2) Pull only a Specific Range of Data from another Workbook
Now the 2nd method.
In the first example above, I am pulling data from every row and column in Sheet1. To do this, I am using the UsedRange property. It doesn’t matter how many tables you have in the source file. It will pull every data from it.
However, you can limit the amount of data that you want to extract from the source file. All you need to do is, specify a range.
Let us assume you want to pull or extract data from the 2nd column (B column) in Sheet1 only. You can use this code.
Sub readExcelData(sTheSourceFile)
On Error GoTo ErrHandler
Application.ScreenUpdating = False ' Do not update the screen.
Dim src As Workbook
Set src = Workbooks.Open(sTheSourceFile, True, True) ' Open the source file.
Dim iRowsCount As Integer
With src.Worksheets("sheet1")
iRowsCount = .Range("B1:B" & .Cells(Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row).Rows.Count
End With
Dim iCnt As Integer ' Just a counter.
For iCnt = 1 To iRowsCount
Cells(iCnt, 1) = src.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("B" & iCnt).Formula
Next iCnt
' Close the source file.
src.Close False ' False, so you don't save the source file.
Set src = Nothing
ErrHandler:
Application.EnableEvents = True
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubI have used the Range() method in this example, to specify the range from where I’ll pull the data. The FileDialog() method remains the same.
👉 Now, if you want to pull data from multiple files and show it in a single file but different sheets, you should read this post. 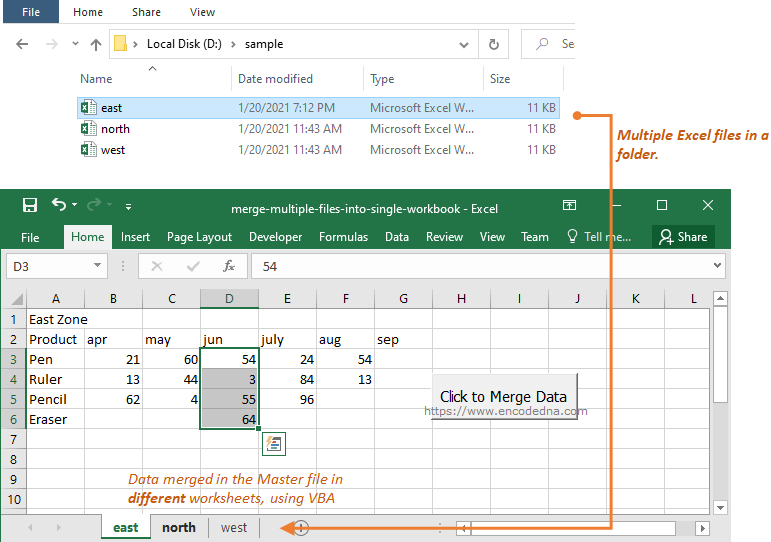
3) Macro to Pull Data from Multiple Sheets from another Workbook
The 3rd method.
The macro to pull data from multiple sheets from another workbook is very simple. However, the method that I am sharing here is slightly different from the first two examples that I have explained above.
Let’s see the code first.
Option Explicit
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
' Create and set the file dialog object.
Dim fd As Office.FileDialog
Set fd = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker)
With fd
.Filters.Clear
.Title = "Select an Excel File"
.Filters.Add "Excel Files", "*.xlsx?", 1
.AllowMultiSelect = false
Dim sFilePath As String
If .Show = True Then
sFilePath = .SelectedItems(1)
End If
End With
If sFilePath <> "" Then
readExcelData (sFilePath)
End If
End Sub
Sub readExcelData(sTheSourceFile)
On Error GoTo ErrHandler
Application.ScreenUpdating = False ' Do not update the screen.
Dim src As Workbook
Set src = Workbooks.Open(sTheSourceFile, True, True) ' Open the source file.
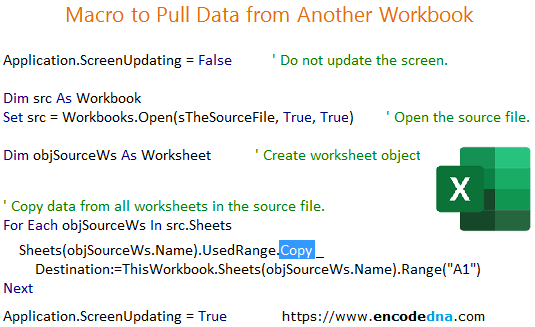
Dim objSourceWs As Worksheet ' Create worksheet object.
' Pull data from all work sheets in the source file.
For Each objSourceWs In src.Sheets
' Check if worksheet exists in the destination file (the current workbook).
If Not chkWorkSheetExists(objSourceWs.Name) Then
' If worksheet does not exists, create a new worksheet.
ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add After:=ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Count)
End If
' Copy data from source to destination.
Sheets(objSourceWs.Name).UsedRange.Copy _
Destination:=ThisWorkbook.Sheets(objSourceWs.Name).Range("A1")�
Next
' Close the source file.
src.Close False ' False, so you don't save the source file.
Set src = Nothing
ErrHandler:
Application.EnableEvents = True
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
' Check if worksheets exists.
Function chkWorkSheetExists(sSheetName As String) As Boolean
On Error Resume Next
Dim sSht As Worksheet
Set sSht = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(sSheetName)
chkWorkSheetExists = Not sSht Is Nothing ' Return true is worksheets exists.
End FunctionUsing the file dialog method you can choose an Excel workbook, which has data in multiple worksheets. The data extraction part is inside the procedure readExcelData().
Once I open the source file, I’ll loop through each sheet and copy data as it is (from its used range) to the destination workbook.
' Pull data from all work sheets in the source file. For Each objSourceWs In src.Sheets ' Copy data from source to destination. Sheets(objSourceWs.Name).UsedRange.Copy _ Destination:=ThisWorkbook.Sheets(objSourceWs.Name).Range("A1") Next
That’s it.
I have shared three different methods here to explain how to pull data from another workbook using Macro. You got different methods for different requirement. My favorite however, is the third method, where it simply copies data from multiple sheets and writes in the destination workbook.
You can similar methods to pull data from multiple Excel workbooks and write it in your destination workbook.
