What this Macro will do?
I wrote this program for my wife. She is teacher. She asked me if there's a simple way to copy and paste contents from a word file to Excel (as it is). Since it’s a repeated job, I said we can automate the process using VBA. However, just make sure the contents are written properly in the word file, that is, the spaces, the next line (carriage return) etc. is nicely done.
In-addition, the macro will read every text in the word file as it is, with the font name, the color of the text, size of the font, it will check if the text is underlined, or if its bold etc.
See this image. 👇
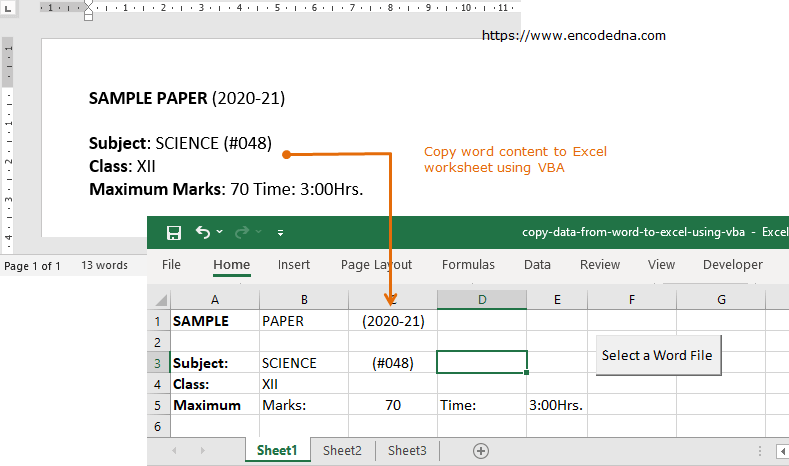
In this example, I have a button, an ActiveX Control in my worksheet (sheet 1). Clicking the button will open a File Picker dialog box, so you can select the word file you want.
Once you have selected the word file, the macro will open the doc, read and extract data (content) from the file and write it in your Excel worksheet.
Note: The file picker or file dialog is optional. You can provide the file name and path to a variable.
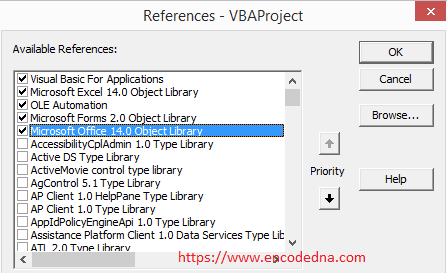
Press Alt+F11 to open the VBA editor. You can also right click sheet1 and choose View Code option. Add Office Object Library Reference to your application. See the image.
Do you know you can import your Outlook emails easily into a Word document using VBA? Check this out.
Option Explicit
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
extract_word_data
End Sub
Public Sub extract_word_data()
On Error Resume Next
' Create a "FileDialog" object as a File Picker dialog box.
Dim fd As Office.FileDialog
Set fd = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker)
Dim sfileName As String
With fd
.AllowMultiSelect = False
.Filters.Clear
.Title = "Select a Word File"
.Filters.Add "All Word Documents", "*.doc?", 1
If .Show = True Then
sfileName = Dir(.SelectedItems(1)) ' Get the file.
End If
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
If Trim(sfileName) <> "" Then
Dim oWord As Object ' Create a Word object.
Set oWord = CreateObject("Word.Application")
oWord.Visible = False ' Do not show the Word file.
' CREATE A DOCUMENT OBJECT.
Dim oDoc
Set oDoc = oWord.Documents.Open(fd.InitialFileName & sfileName)
Dim sPara() As String
sPara = Split(oDoc.range, vbCr) ' split the carriage returns and store in the variable.
Dim iParaCount, iCnt1, iRow As Integer ' Just counters.
iRow = 1
Dim txt As String
For iParaCount = 0 To UBound(sPara)
Dim str() As String
str = Split(sPara(iParaCount), " ") ' split the spaces and store in the variable.
For iCnt1 = 0 To UBound(str)
txt = Replace(str(iCnt1), "", "")
Sheet1.Cells(iRow, iCnt1 + 1) = txt ' Write data.
If (Trim(txt <> "")) Then
' get text properties like font size, font name, color and underline (if any)
'and assign it to the text on the WorkSheet.
With oDoc.range.Paragraphs(iRow).range.Words(iCnt1 + 1)
Sheet1.Cells(iRow, iCnt1 + 1).Font.Size = .Font.Size
Sheet1.Cells(iRow, iCnt1 + 1).Font.Name = .Font.Name
Sheet1.Cells(iRow, iCnt1 + 1).Font.Color = .Font.Color
If (.Font.Bold) Then
Sheet1.Cells(iRow, iCnt1 + 1).Font.Bold = .Font.Bold
End If
If (.Font.Underline) Then ' if the text is underlined.
Sheet1.Cells(iRow, iCnt1 + 1).Font.Underline = xlUnderlineStyleSingle
End If
End With
End If
DoEvents
Next iCnt1
iRow = iRow + 1
Next iParaCount
End If
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
' Clean up.
oWord.Close
oWord.Quit
oDoc.Quit
Set oWord = Nothing
Set oDoc = Nothing
End SubNote: The file picker or file dialog is optional. You can provide the file name and path to the variable sfileName.
The code above has comments to help you understand the functions.
The macro has some limitations, of-course. For example, it may not translate the tab spaces properly, that is, if you have used the tab multiple times to shift a particular string from left to right etc. However, it will read the spaces and carriage returns (for next line) along with font name, size, color of the text, underline etc.
Copy table data from Word file to Excel Worksheet (as it is)
Now, a word file or doc may have tables (multiple tables). You can read those tables as it is using a simple macro. Here’s the example.
You can test the above code using big word files, with many paragraphs, tables and other objects.
Conclusion
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a powerful tool that can be used for a wide range of tasks beyond copying data from Word to Excel. You can use VBA for Data Analysis, Report Generation, Web Scraping and Automate data entry tasks, to name a few.
