Why use Media Queries?
We use CSS3 media queries for responsive web designing (such as mobiles or tablets) to apply different styles for different media types. The queries use @media rule and it is defined inside the <style> tag in a web page or in .css files.
Usually, we use a media query like this,
<style>
.myClass {
font-size: 30px;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 500px)
{
.myClass { font-size: 20px; }
}
</style>It means, if the screen or the browser window is 500px or smaller.
Width Between Two Values
Here's a DIV element with default style
<style> .intro { position: relative; top: 50px; color: red; } </style> <body> <div class='intro' Hello, I am Arun Banik! </div> </body>
This is the default style and it looks similar in all devices.
However, I want to assign a different class or different attributes (or values) for the <div> element, when the width is between 350px and 600px.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <style> .intro { position: relative; top: 50px; color: red; } @media screen and (min-width: 350px) and (max-width: 600px) { .intro { top: 0; color: green; font-size: 20px; } } </style> </head> <body> <div class='intro'> Hello, I am Arun Banik! </div> </body> </html>
Now see the media query in the above example. It has two values min-width and max-width. So, the new values appears (or the values changes) when the screen width is between 350px and 600px. Or else, the screen takes the default values (see the .intro class).
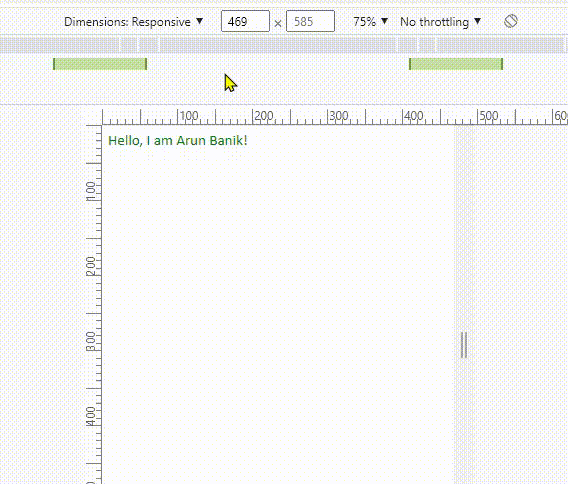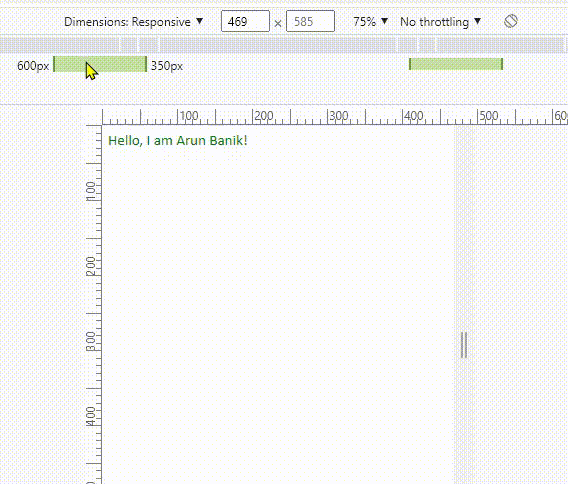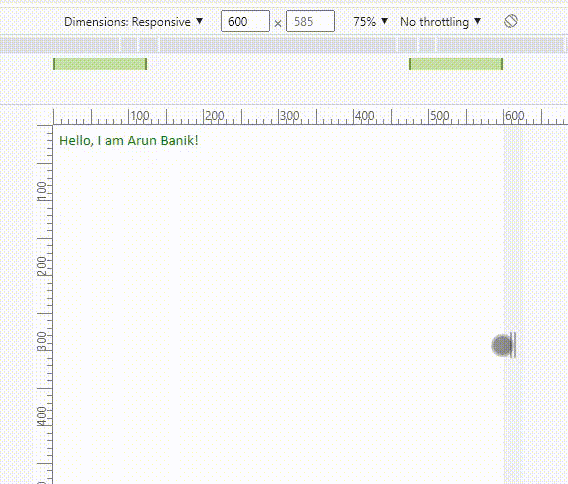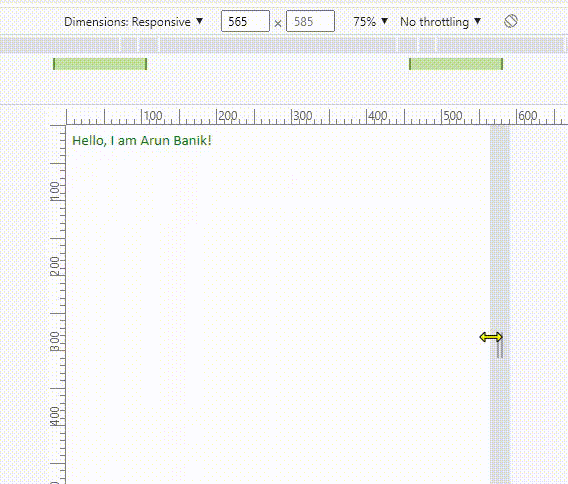
Note: Do not forget to add this line inside the <head> tag when you are using media queries.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
You must add the viewport to allow browsers to render responsive pages. The media queries will not work if you have not added the viewport.
