Last updated: 19th June 2024
A DataGridView control in .Net is perfect for showing data in a tabular format. Its use is not limited to just displaying data, but it’s a perfect tool for doing data manipulation by binding it with a database. With its many useful features, you can make the DataGridView to perform like an Excel spreadsheet. Here this article, I'll show how to bind a ComboBox in a DataGridView control dynamically.Update: See code for C#. I have also explained how to set the name property of each column in the DataGridView and its proper usage.
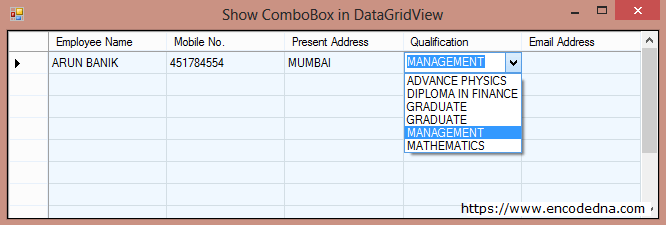
The ComboBox will show up in a Cell of a particular column when focus sets on that column. See above image. This will allow users to select value from a list of pre-define of items.
Follow these steps.
Start "Microsoft Visual Studio" and select a "New Project' from the File menu (Left Top Menu).
From "New Project" templates, select Windows Forms Application and click OK.
01) A new project appears with a "Blank Form". Click the Toolbox button (or press Ctrl+Alt+X keys) to open Toolbox window. Under All Windows Forms, find DataGridView control and "double click" it to add the control in the form.

02) Select the DataGridView control and "right click" the mouse to choose Properties. In the Properties window, find the Columns property (under "Misc") and open it. Add few columns like "Employee Name", "Mobile No." etc to the Grid. (See the below Image 👇).

To add the columns, simply click the Add button, which will open the "Add Column" window. You will have to add values to the first and last fields, "Name" and "Header Text".
Remember, the "Present Address" column is important for this example to work properly. Therefore, in the "Header Text" field add the text Present Address and in the Name field add "PresentAddress" (without any space).
03) Finally drag and drop a ComboBox control on the DataGridView. The ComboBox will have a list of Qualifications. So add a few items in the ComboBox. To add the values, right click the control and choose Properties. Find the Items property and add items to it.
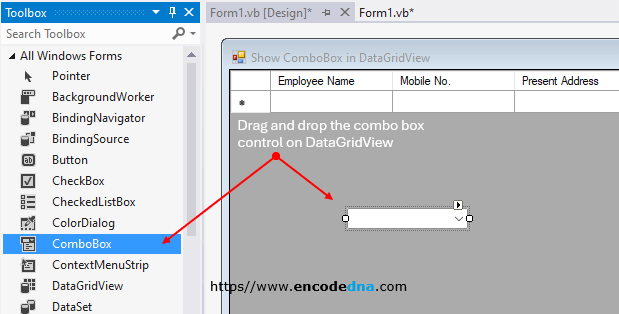
Set the Visible property of the ComboBox as "False". We don’t want the ComboBox to be visible when the form loads. The ComboBox will show up when the focus is on a Cell of Qualification column. Until then, it remains hidden.
Note: The "ComboBox" control should be placed on the "DataGridView" control.
Now, let’s write the code.
Copy and paste the below code in the code window of your application and run the application.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { public partial class frmDataGridView_Demo : Form { DataTable dtTable = new DataTable("Employee"); // CREATE A DATATABLE. public frmDataGridView_Demo() { InitializeComponent(); addRows(); // ADD FEW BLANK ROWS TO START WITH. } private void addRows() { DataRow row = null; row = dtTable.NewRow(); int iCntCol = 0; for (iCntCol = 1; iCntCol <= 10; iCntCol++) { row = dtTable.NewRow(); // ADD BLANK ROWS TO THE DATATABLE. dtTable.Rows.Add(row); } // ADD DATATABLE TO GRID. (WITH THE BLANK ROWS) dataGridView1.DataSource = dtTable; // ADD SOME COLOR TO THE GRID. dataGridView1.GridColor = Color.FromArgb(211, 222, 229); dataGridView1.BackgroundColor = Color.Wheat; dataGridView1.RowsDefaultCellStyle.BackColor = Color.AliceBlue; dataGridView1.RowsDefaultCellStyle.SelectionBackColor = Color.CornflowerBlue; dataGridView1.RowsDefaultCellStyle.SelectionForeColor = Color.White; } // CONTROL THE KEY STROKES. protected override bool ProcessCmdKey(ref System.Windows.Forms.Message msg, System.Windows.Forms.Keys keyData) { if (keyData == Keys.Enter) { // ON ENTER KEY, GO TO THE NEXT CELL. // WHEN THE CURSOR REACHES THE LAST COLUMN, CARRY IT ON TO THE NEXT ROW. if (ActiveControl.Name == "DataGridView1") { // CHECK IF ITS THE LAST COLUMN if (dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex == dataGridView1.ColumnCount - 1) { // GO TO THE FIRST COLUMN, NEXT ROW. dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.RowIndex + 1] .Cells[0]; } else { // NEXT COLUMN. dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index] .Cells[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1]; } return true; } else if (ActiveControl is DataGridViewTextBoxEditingControl) { // SHOW THE COMBOBOX WHEN FOCUS IS ON A CELL CORRESPONDING TO THE "QUALIFICATION" COLUMN. if (dataGridView1.Columns [dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex].Name == "PresentAddress") { dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index] .Cells[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1]; // SHOW COMBOBOX. Show_Combobox(dataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index, dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex); SendKeys.Send("{F4}"); // DROP DOWN THE LIST. return true; } else { // CHECK IF ITS THE LAST COLUMN. if (dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex == dataGridView1.ColumnCount - 1) { // GO TO THE FIRST COLUMN, NEXT ROW. dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.RowIndex + 1] .Cells[0]; } else { // NEXT COLUMN. dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index] .Cells[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1]; } return true; } } else if (ActiveControl.Name == "ComboBox1") { // HIDE THE COMBOBOX AND ASSIGN COMBO'S VALUE TO THE CELL. comboBox1.Visible = false; dataGridView1.Focus(); // ONCE THE COMBO IS SET AS INVISIBLE, SET FOCUS BACK TO THE GRID. (IMPORTANT) dataGridView1[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex, dataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index].Value = comboBox1.Text; dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index] .Cells[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1]; } else { SendKeys.Send("{TAB}"); } return true; } else if (keyData == Keys.Escape) // PRESS ESCAPE TO HIDE THE COMBOBOX. { if (ActiveControl.Name == "ComboBox1") { comboBox1.Text = ""; comboBox1.Visible = false; dataGridView1.CurrentCell = dataGridView1.Rows[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.RowIndex] .Cells[dataGridView1.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex]; dataGridView1.Focus(); } return true; } else { return base.ProcessCmdKey(ref msg, keyData); } } private void Show_Combobox(int iRowIndex, int iColumnIndex) { // DESCRIPTION: SHOW THE COMBO BOX IN THE SELECTED CELL OF THE GRID. // PARAMETERS: iRowIndex - THE ROW ID OF THE GRID. // iColumnIndex - THE COLUMN ID OF THE GRID. int x = 0; int y = 0; int Width = 0; int height = 0; // GET THE ACTIVE CELL'S DIMENTIONS TO BIND THE COMBOBOX WITH IT. Rectangle rect = default(Rectangle); rect = dataGridView1.GetCellDisplayRectangle(iColumnIndex, iRowIndex, false); x = rect.X + dataGridView1.Left; y = rect.Y + dataGridView1.Top; Width = rect.Width; height = rect.Height; comboBox1.SetBounds(x, y, Width, height); comboBox1.Visible = true; comboBox1.Focus(); } } }
When the focus is the fourth cell, the combo will automatically show a list of "qualification".
Option Explicit On
Public Class frmDataGridView_Demo
Dim dtTable As New DataTable("Employee") ' CREATE A DATATABLE.
Private Sub frmDataGridView_Demo_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
AddRows() ' ADD FEW BLANK ROWS TO START WITH.
End Sub
Private Sub AddRows()
Dim row As DataRow
row = dtTable.NewRow
For iCntCol = 1 To 10
row = dtTable.NewRow ' ADD BLANK ROWS TO THE DATATABLE.
dtTable.Rows.Add(row)
Next
With DataGridView1
.DataSource = dtTable ' ADD DATATABLE TO GRID. (WITH THE BLANK ROWS)
' JUST FOR THE LOOKS.
.GridColor = Color.FromArgb(211, 222, 229)
.BackgroundColor = Color.Wheat
.RowsDefaultCellStyle.BackColor = Color.AliceBlue
.RowsDefaultCellStyle.SelectionBackColor = Color.CornflowerBlue
.RowsDefaultCellStyle.SelectionForeColor = Color.White
End With
End Sub
' CONTROL THE KEY STROKES.
Protected Overrides Function ProcessCmdKey(ByRef msg As System.Windows.Forms.Message, _
ByVal keyData As System.Windows.Forms.Keys) As Boolean
If keyData = Keys.Enter Then
' ON ENTER KEY, GO TO THE NEXT CELL.
' WHEN THE CURSOR REACHES THE LAST COLUMN, CARRY IT ON TO THE NEXT ROW.
If ActiveControl.Name = "DataGridView1" Then
With DataGridView1
If .CurrentCell.ColumnIndex = .ColumnCount - 1 Then ' CHECK IF ITS THE LAST COLUMN
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentCell.RowIndex + 1).Cells(0) ' GO TO THE FIRST COLUMN, NEXT ROW.
Else
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentRow.Index).Cells(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1) ' NEXT COLUMN.
End If
End With
ElseIf TypeOf ActiveControl Is DataGridViewTextBoxEditingControl Then
' SHOW THE COMBOBOX WHEN FOCUS IS ON A CELL CORRESPONDING TO THE "QUALIFICATION" COLUMN.
With DataGridView1
If .Columns(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex).Name = "PresentAddress" Then
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentRow.Index).Cells(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1)
' SHOW COMBOBOX.
Show_Combobox(.CurrentRow.Index, .CurrentCell.ColumnIndex)
SendKeys.Send("{F4}") ' DROP DOWN THE LIST.
Else
If .CurrentCell.ColumnIndex = .ColumnCount - 1 Then ' CHECK IF ITS THE LAST COLUMN
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentCell.RowIndex + 1).Cells(0) ' GO TO THE FIRST COLUMN, NEXT ROW.
Else
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentRow.Index).Cells(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1) ' NEXT COLUMN.
End If
End If
End With
ElseIf ActiveControl.Name = "ComboBox1" Then
' HIDE THE COMBOBOX AND ASSIGN COMBO'S VALUE TO THE CELL.
ComboBox1.Visible = False
With DataGridView1
.Focus() ' ONCE THE COMBO IS SET AS INVISIBLE, SET FOCUS BACK TO THE GRID. (IMPORTANT)
.Item(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex, .CurrentRow.Index).Value = Trim(ComboBox1.Text)
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentRow.Index).Cells(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex + 1)
End With
Else
SendKeys.Send("{TAB}")
End If
Return True
ElseIf keyData = Keys.Escape Then ' PRESS ESCAPE TO HIDE THE COMBOBOX.
If ActiveControl.Name = "ComboBox1" Then
ComboBox1.Text = "" : ComboBox1.Visible = False
With DataGridView1
.CurrentCell = .Rows(.CurrentCell.RowIndex).Cells(.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex)
.Focus()
Return True
End With
End If
Else
Return MyBase.ProcessCmdKey(msg, keyData)
End If
End Function
Private Sub Show_Combobox(ByVal iRowIndex As Integer, ByVal iColumnIndex As Integer)
' DESCRIPTION: SHOW THE COMBO BOX IN THE SELECTED CELL OF THE GRID.
' PARAMETERS: iRowIndex - THE ROW ID OF THE GRID.
' iColumnIndex - THE COLUMN ID OF THE GRID.
Dim x As Integer = 0
Dim y As Integer = 0
Dim Width As Integer = 0
Dim height As Integer = 0
' GET THE ACTIVE CELL'S DIMENTIONS TO BIND THE COMBOBOX WITH IT.
Dim rect As Rectangle
rect = DataGridView1.GetCellDisplayRectangle(iColumnIndex, iRowIndex, False)
x = rect.X + DataGridView1.Left
y = rect.Y + DataGridView1.Top
Width = rect.Width
height = rect.Height
With ComboBox1
.SetBounds(x, y, Width, height)
.Visible = True
.Focus()
End With
End Sub
End Class